This perspective focuses on illustrating the underappreciated connections between reactive carbonyl species (RCS), preliminary binding in the nonenzymatic glycation (NEG) course of, and nonenzymatic covalent protein modification (right here termed NECPM).
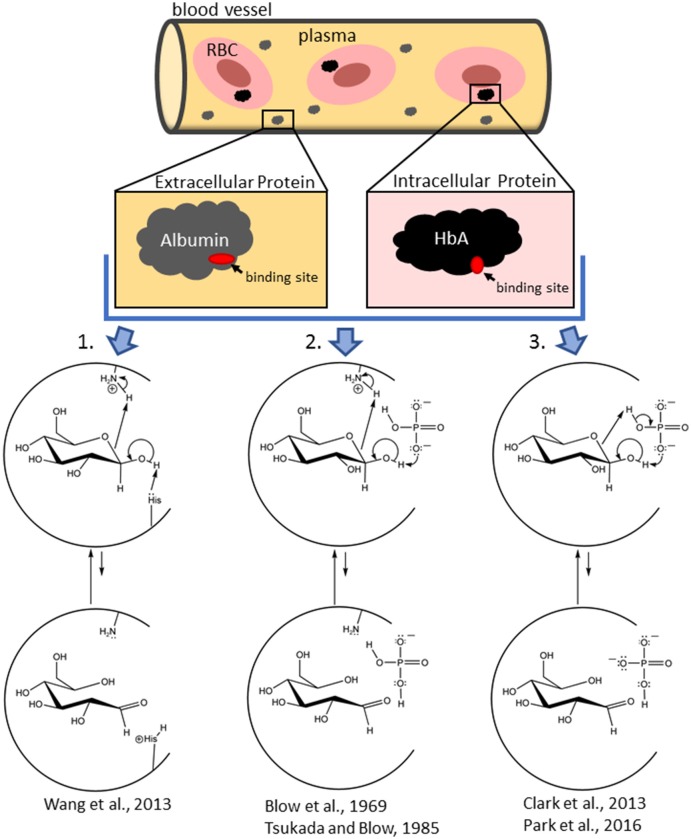
While glucose is the central species concerned in NEG, latest research point out that the initially-bound glucose species in the NEG of human hemoglobin (HbA) and human serum albumin (HSA) are non-RCS ring-closed isomers.
The ring-opened glucose, an RCS construction that reacts in the NEG course of, is most probably generated from previously-bound ring-closed isomers present process concerted acid/base reactions whereas sure to protein.
The technology of the glucose RCS can contain concomitantly-bound physiological species (e.g., inorganic phosphate, water, and so on.); right here termed effector reagents. Extant NEG schemes don’t account for these latest findings.
In addition, effector reagent reactions with glucose in the serum and erythrocyte cytosol can generate RCS (e.g., glyoxal, glyceraldehyde, and so on.). Recent analysis has proven that these RCS covalently modify proteins in vivo by way of NECPM mechanisms. A basic scheme that displays each the reagent and mechanistic range that may result in NEG and NECPM is offered right here.
A perspective that accounts for the relationships between RCS, NEG, and NECPM can facilitate the understanding of web site selectivity, might assist clarify general glycation charges, and might have implications for the scientific evaluation/management of diabetes mellitus.
In view of this attitude, concentrations of ribose, fructose, Pi, bicarbonate, counter ions, and the ensuing RCS generated inside intracellular and extracellular compartments could also be of significance and of scientific relevance. Future analysis can also be proposed.
Factors affecting urine reagent strip blood outcomes in canine and nonhuman primates and interpretation of urinalysis in preclinical toxicology research: a Multi-Institution Contract Research Organization and BioPharmaceutical Company Perspective.
BACKGROUNDUrinalysis information in preclinical toxicology research could be influenced by preanalytic and analytic components which have the potential to confound interpretation. There is a paucity of data concerning optimistic reagent strip urinary blood reactions in wholesome nonhuman primates (NHP) and Beagle canine used in preclinical toxicology research.
OBJECTIVEThe goals have been (1) to determine historic management information for reagent strip urinary blood reactions in wholesome NHP and Beagle canine, (2) to find out the incidence of optimistic urinary blood reactions throughout predose and dosing phases, and (3) to find out if assortment apply was a related parameter.
METHODSHistorical management information from 2 establishments in the biopharmaceutical trade have been retrospectively analyzed for reagent strip urinary blood reactions in wholesome NHP and Beagles.
The incidence of optimistic outcomes between the two establishments with completely different urine assortment practices and between males and females was in contrast.
RESULTSThe incidence of optimistic urinary blood reactions in NHP was comparable between establishments (≤ 14% in males; ≤ 33% in females), whereas the incidence of optimistic urinary blood reactions in Beagles was extra variable (≤ 77% in males; ≤ 69% in females), and increased in females throughout the dosing part.
CONCLUSIONSPositive urinary blood outcomes that would doubtlessly be misinterpreted as toxicologically related have been recognized in wholesome NHP and Beagles throughout predose and dosing phases.
Different incidences of optimistic outcomes between the two establishments have been doubtless associated to assortment practices. Strategies to scale back feces and meals contamination of collected urine samples ought to assist reduce false-positive urinary blood reactions.

